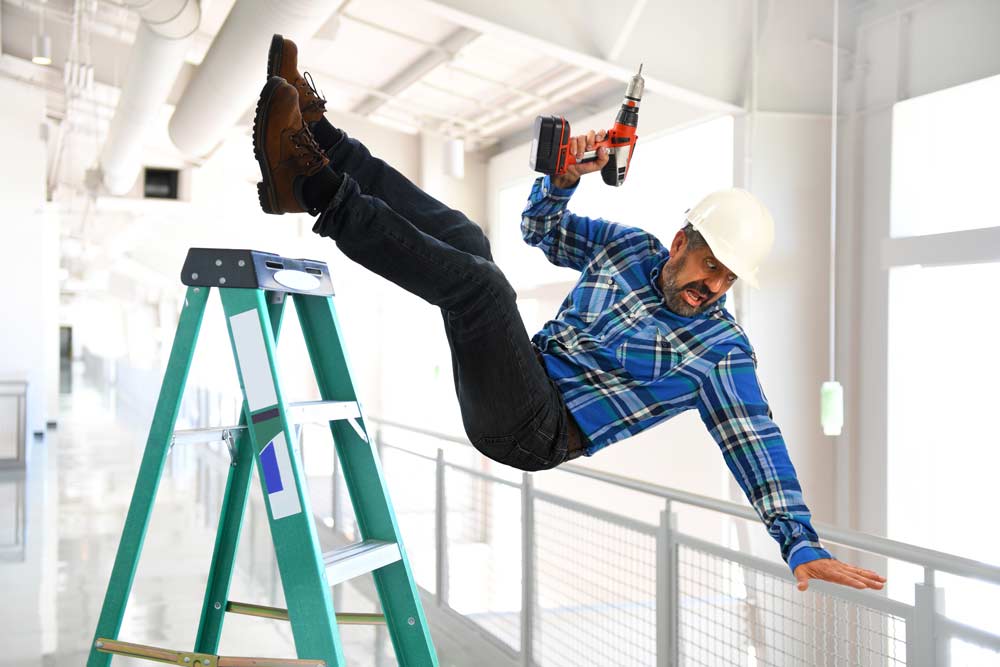
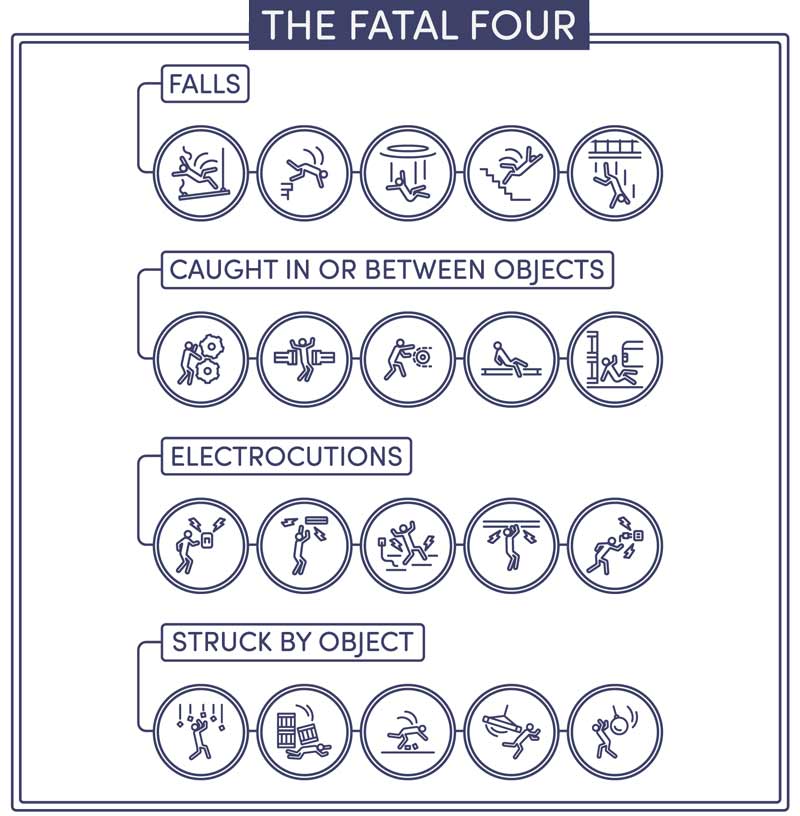
The four most frequent causes of death on construction sites have been labeled by OSHA as the “Fatal Four.” There were 5,333 deaths in 2019 alone that occurred as a result of fatal occupational injuries. The causes for death are listed here in order with the most first – Falls, Being struck by an object, Being electrocuted, Getting caught in between equipment and machines. Be sure to follow OSHA’s guidelines.
Tag Archives: Construction Safety
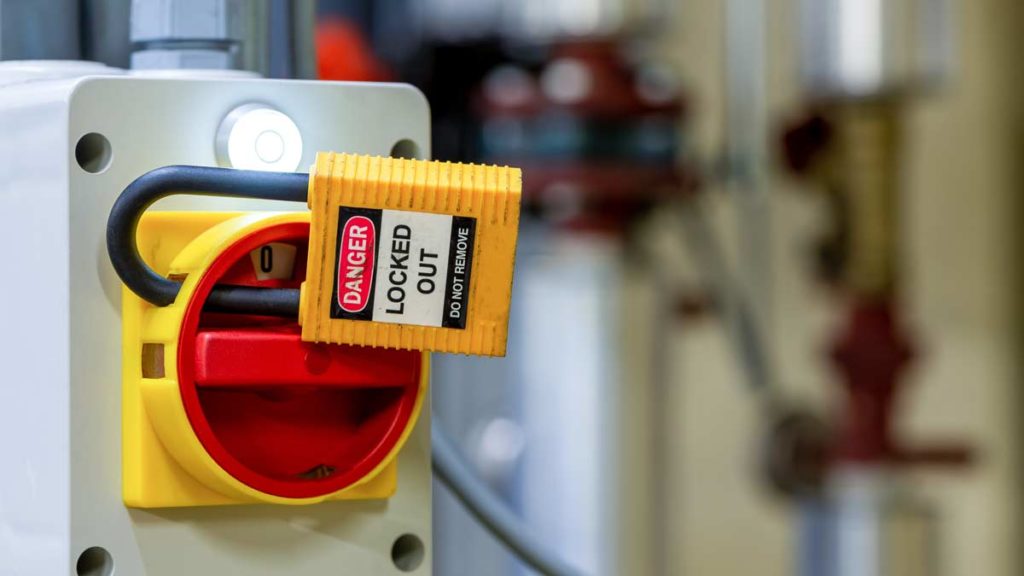
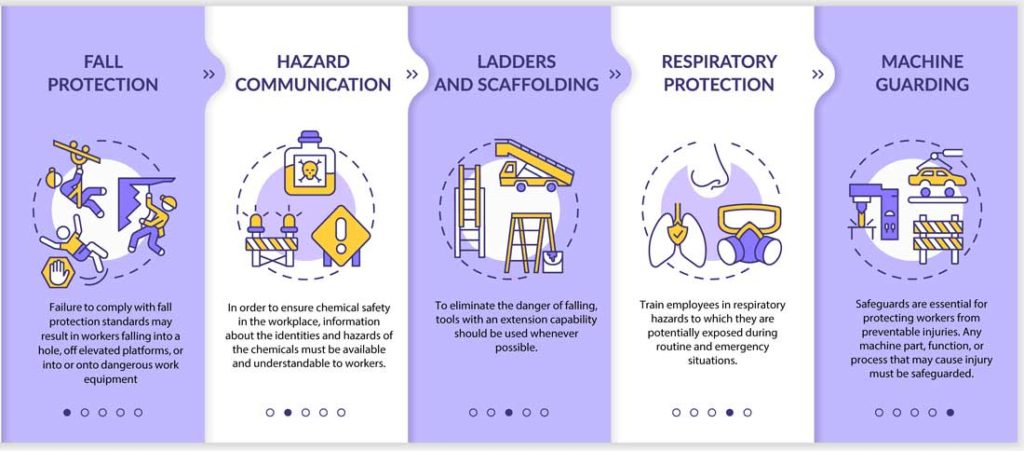
The control of hazardous energy as pertaining to lockout-tagout had over 2,000 violations in 2020. The purpose of controlling hazardous energy in this manner is to reduce/erase the potential harm to employees during the servicing and maintenance of machines and equipment in which the unexpected energization or start up of the machines or equipment, or the release of stored energy.
Ladders had over 2,000 violations cited in 2020. The regulations placed on the use of ladders on work sites is to diminish the risk of an employee becoming injured. OSHA has many specific rules for different ladders and work areas in the construction field. Some rules are how much weight a ladder can bear, using ladders together for extra height, and ladder care and maintenance.
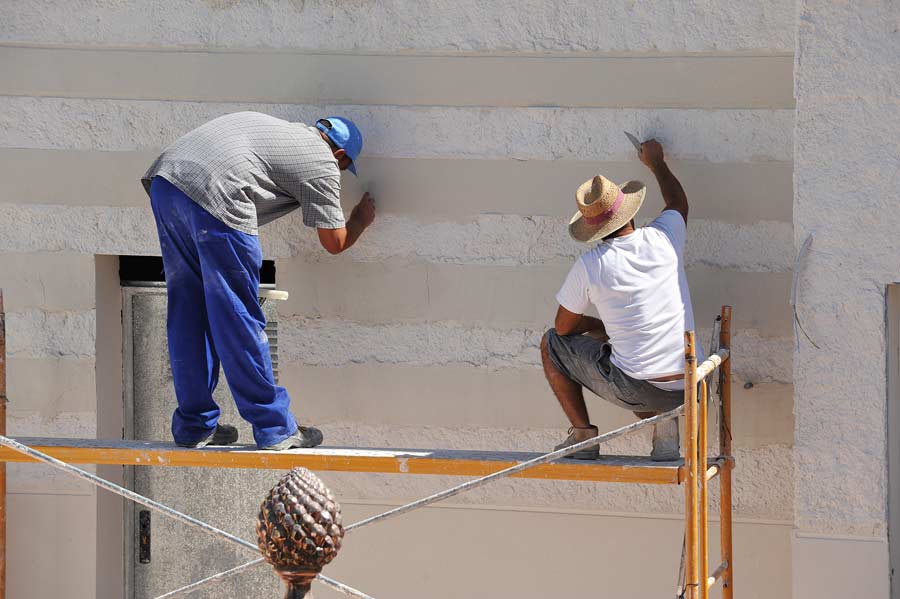
Scaffolding requirements had over 2,500 violations cited in 2020. A scaffold should be capable of supporting its own weight and at least four times the maximum intended load to be applied to the scaffold. It may be necessary to consult an engineer to determine heavy-load points to prevent injury from occurring. Two main type of injuries that can occur from scaffolding violations are falling and either landing feet or head first. An employer at a construction site should
include a review of the scaffolding system,censure that workers have appropriate safety equipment, and place supervisors in charge that have the skill, experience, and training to ensure safe installation and dismantling according to the scaffolding manufacturer’s specifications.
OSHA established standards to protect workers against respiratory conditions resulting from contaminated jobsites. Respiratory Protection had over 2,500 cited violations in 2020. The purpose of this standard is to prevent atmospheric contamination of the workplace and to reduce the chance of breathing in air contaminated with harmful dusts, fogs, fumes, mists, gasses, smokes, sprays, or vapors.
OSHA established standards to protect workers against hazardous chemical exposure on the jobsite. If an employer fails to follow these safety regulations, it is foreseeable that an employee or others could inhale hazardous material or come into physical bodily contact with the chemicals themselves.
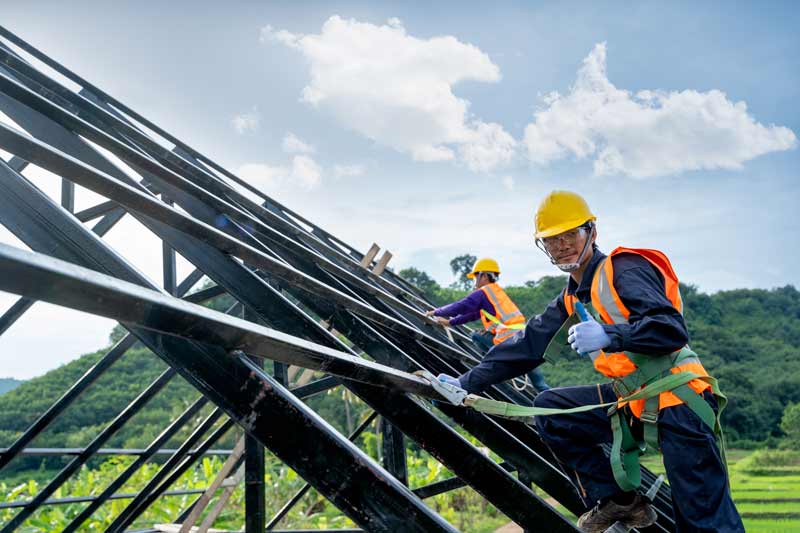
To eliminate the danger of falling, tools with an extension capability should be used whenever possible. However, when workers cannot avoid working from heights (defined as six feet or more for the construction industry) OSHA has safety requirements put in place to protect workers from predictable dangers.
OSHA standards exist to protect workers from unsafe conditions in the work place. When workers suffer injuries on the jobsite, those people in charge of safety at the jobsite may be responsible for the consequences of failing to protect workers from these foreseeable dangers.