What is Whiplash?
Many clients who are involved in a motor vehicle collision are diagnosed with “whiplash.” The purpose of this article is to explain the mechanism of injury, symptoms, anatomy, diagnosis and treatment of this condition.
Whiplash refers to a soft tissue injury of the neck. It commonly occurs after a car accident and is also known in the medical community as a neck strain or sprain. The mechanism of injury is a sudden backward and/or forward jerking motion of the head (also known as Cervical Acceleration-Deceleration).
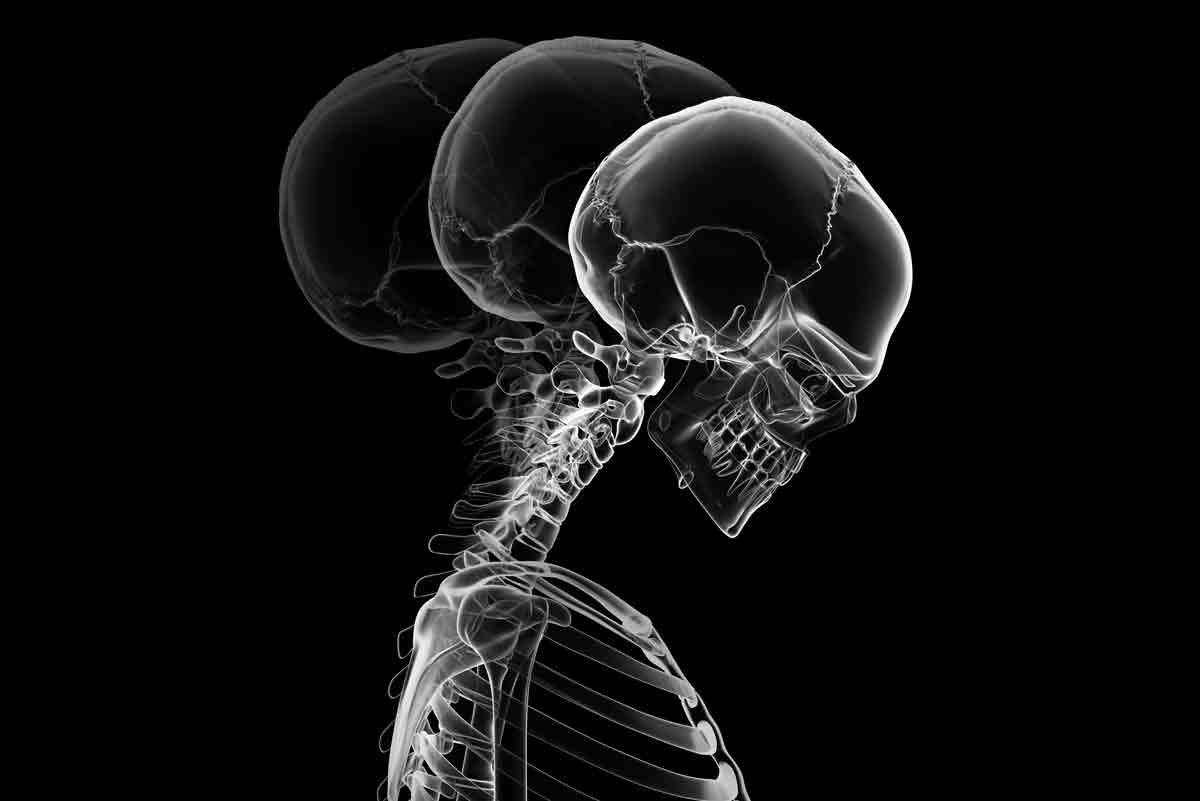
Whiplash Symptoms
Symptoms may occur immediately or may be delayed for several days after the incident.
Whiplash symptoms most commonly include:
- Neck pain or stiffness
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Pain and numbness in the arm and/or hand
- Shoulder and/or low back pain
- Memory loss, irritability, sleep disturbance and/or fatigue
Anatomy
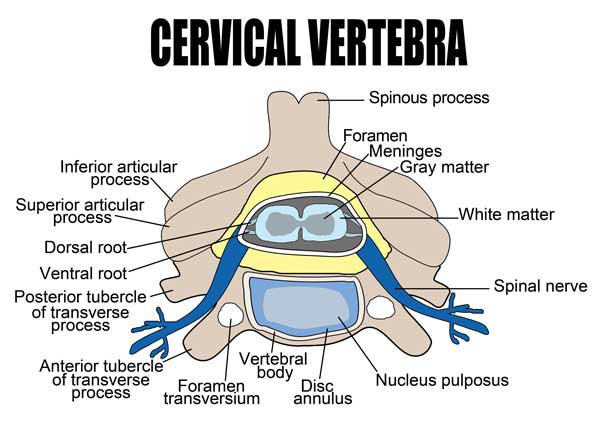
As a soft tissue injury (meaning the injury does not involve the bone), familiarity with the soft tissues around the neck (also known as the cervical spine) can be important in understanding the whiplash condition. The primary structures that are in danger of injury include the nerves, muscles/tendons, ligaments, and intervertebral discs. The major nerves about the neck originate from eight cervical spinal nerve roots.
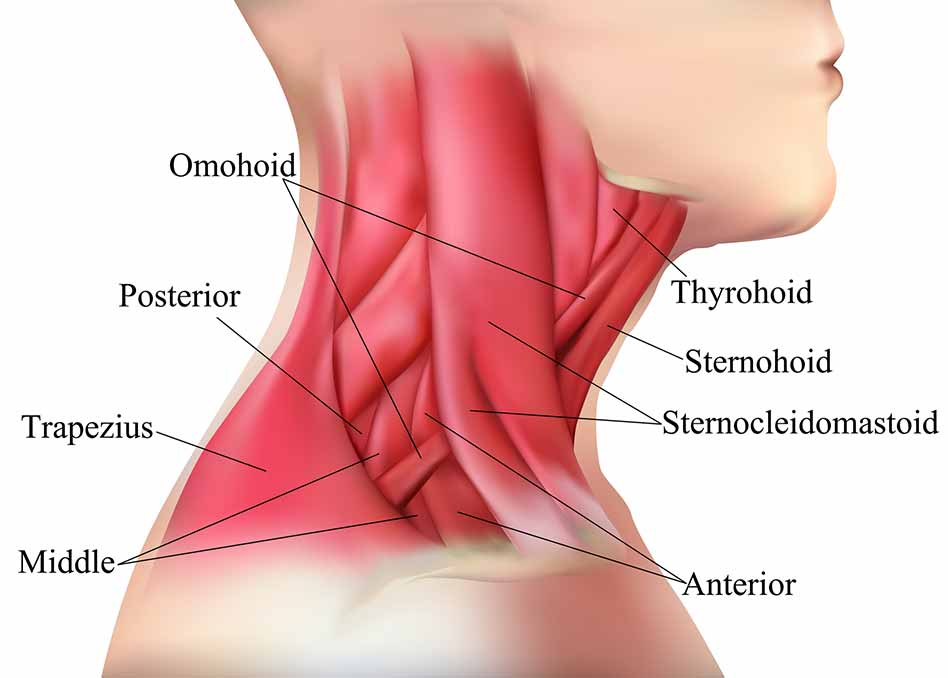
The muscles about the neck are numerous, but the major ones include the sternocleidomastoid, the anterior, middle and posterior scalene muscles, and trapezius.
Ligaments about the cervical spine are also quite complex. On a basic level, they include the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments of the spine, the posterior spinal ligaments and the internal and external ligaments of the craniocervical junction. There are also relevant ligaments about the facet joints where the vertebral bodies articulate posteriorly. Lastly, intervertebral discs refer to the “shock absorbers” that lie between the vertebral bodies of the spine.
The actual names are not as important as understanding the myriad of sources that contribute to the whiplash syndrome. This also helps explain why treatment and treatment outcomes can be varied. Whiplash can involve injury to a number of different structures and to a different degree.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is typically made by a clinical evaluation with a health care provider. Standard X-rays are used to rule out bone fractures but are not useful in the actual diagnosis of whiplash because typically, injury to soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments and/or the intervertebral discs cannot be detected by X-ray alone. Specialized imaging with magnetic resonance imaging and/or CT scans may show intervertebral disc abnormalities.
Whiplash Treatment
Treatment may include pain medications, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen, muscle relaxants, physical therapy, and chiropractic care. Most patients recover in three to six months. There are some, however, who continue to experience lasting neck pain and headaches.
Ask Dr. John, Esq. is an experienced physician and personal injury attorney available to answer medical-legal questions.
Please direct questions or comments to drjohn@dillerlaw.com and/or call (617) 523-7771.
